In this article, we will focus on what makes dApps (decentralized applications) a hot topic among blockchain and crypto users and how Web3 developers can create & build their own dApps by using the latest blockchain technology.
What is a dApp?
First and foremost, what is a dApp? Also known as decentralized applications, dApps are a huge part of the Web3 industry. The dApp market is evolving at an exponential rate, with its market cap level reportedly reaching $368 billion in the next five years.
Essentially, dApps are decentralized applications built on the blockchain (at the moment, the Ethereum blockchain remains the number one choice among Web3 developers). Dapps are a combination of a backend, a frontend and a smart contract. Decentralized applications do not rely on centralized authority, unlike the traditional centralized software. Instead, dApps interact with a blockchain directly.
Simply put, a dApp is an open-source software application which leverages the distributed peer-to-peer blockchain technology.
N.B. Check out GetBlock’s ‘dApps Explained’ guide
Why do developers build on Ethereum?
So what’s the deal with Ethereum? The Ethereum blockchain not only hosts the vast majority of dApps but also it is the second-largest cryptocurrency, succeeded only by Bitcoin, which, in turn, has a more limited number of commands on its development network.
Ethereum is both a beginner and expert-friendly blockchain with smart contract support. It utilizes the Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism; however, the network is switching over to Proof-of-Stake in hopes to make the blockchain more efficient, cheaper and less damaging to the environment. Despite the ongoing issues regarding PoW, Ethereum is strongly holding the first place in the Web3 development sphere.
Now, why do developers tend to go for Ethereum? As stated before, most dApps require the implementation of three core elements - backend, frontend and smart contract. In some ways, the Web3 development does not differ much from its predecessor - Web2. For instance, those who have skills in JavaScript, HTML, CSS, etc. can benefit quickly from their knowledge when it comes to frontend development.
N.B. Here’s how you can become a blockchain developer today
Nevertheless, backend development is a completely different story. We are all familiar with the fact that blockchains are decentralized networks; that means that each dApp developer comes out with a specific infrastructure designed to store “the brains” of the application. Platforms, like GetBlock, can help users save their time and money and help clients ensure a seamless and fast connection between frontend and backend.
What are Smart Contracts?
Smart contract is another crucial byproduct of blockchain technology. In short, smart contracts are digital code-based self-executing agreements that are open to the public ledger. The smart contract technology allows dApps to perform automated transactions and store data on the blockchain when a set of pre-chosen conditions is met.
On top of decentralization and reliability, smart contracts guarantee immediate transaction verification, better speed, efficiency and improved security (thus, smart contacts are encrypted and so are the transactions between peers on the blockchain).
N.B. Here’s GetBlock’s guide on how to use the new smart contract technology
What is Ethereum’s Solidity?
Now, Solidity also deserves a separate shoutout. For Ethereum users, smart contracts are implemented with the help of Solidity - a high-level and contract-oriented programming language designed on the basis of C++, Python and JavaScript to fit the needs of Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
With Solidity, developers are able to build voting contracts, crowdfunding, wallets, and far more. Solidity is a popular choice among developers not only because of its broad toolkit (in terms of dApp development users get a build tool, package management and deployment assistance) but also because it offers thorough documentation in multiple languages where complex features are defined in detail.
How dApps are built
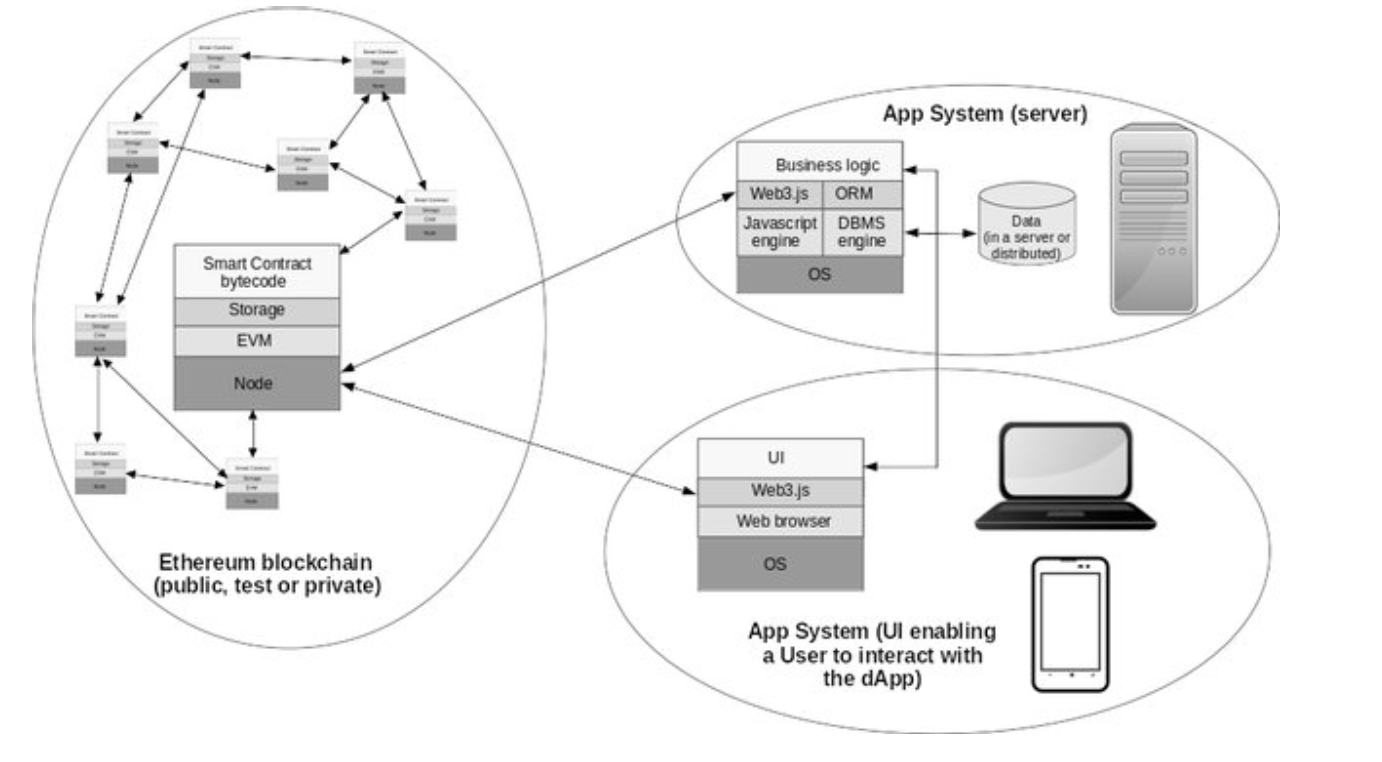
Ethereum dApp Architecture // Source: Research Gate
Install Truffle Framework
Truffle Network is a testing framework and development environment designed to fit the Ethereum Virtual Machine.
Generate boilerplate code
Boilerplate code is used to describe repeatedly replicated sections of code used to provide minor functionality.
Launch Ethereum Node emulator and the truffle command by starting environment development
Compile Solidity contracts into JSON artifacts and deploy the contracts
JSON-RPC is used to describe a stateless remote procedure call (RPC) with JSON employed for payload. JSON-RPC is used by frontend apps to communicate with the Ethereum network
Run and modify your dApp
Run your dApp in the browser and establish interaction with Ethereum by getting a handle on the Web3 object and setting the provider.
This is only the foundation of a potential dApp; for details please check the official Truffle documentation.
Bottom line
Despite the fact that dApps are a fairly new product on the market, the blockchain industry has already benefited from them in a major way. Not only do decentralized applications increase the activity in the digital community, they also set high standards for developers, pushing them to focus on security, transparency, availability and seamlessness. Some of the most popular dApp examples include:
- DeFi projects (PancakeSwap, SushiSwap, Kyber Network);
- GameFi (Axie Infinity, The Sandbox, Cryptokitties, Zed Run);
- Marketplaces (Magic Eden, OpenSea, AtomicMarket, Axie Marketplace).