Best Crypto Bridges 2025: Tested & Compared

Vance Wood
November 17, 2025
7 min read

One of the primary concerns of the Web3 ecosystem is its inevitable fragmentation between various chains. They are suited for different tasks, and while Web3 developers do their best for compatibility, sending assets between them can often be a non-trivial task. That’s why we need tools that do exactly that—and our article is about them.
Check GetBlock nodes, with more than 100 available chains, for extra compatibility.
Best crypto bridges: List
Today, we’ll overview seven bridging protocols, each of which uses a combination of different working principles:
Wormhole
Stargate
Synapse
Orbiter
Axelar
Router
Rubic
Before exploring them further, let’s see what blockchain bridges are and how they usually work.
What is a crypto bridge
Blockchain bridges are tools for transferring crypto assets across blockchains, making the Web3 world interoperable. They are different in functionality, but most of them support the widespread tokens, such as USDT, USDC, ETH (for EVM chains), and popular wrapped tokens.
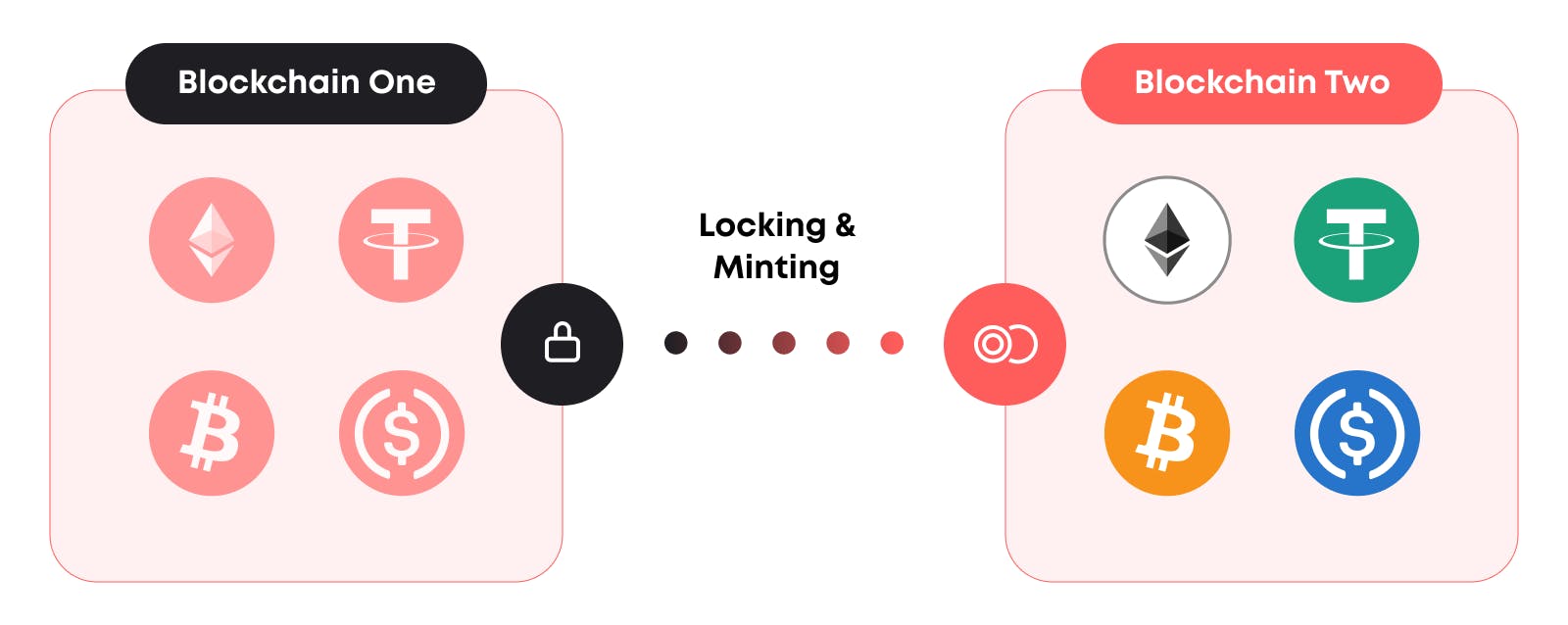
Let’s see what wrapping is and how bridges operate in general.
How do crypto bridges work
Blockchain bridges utilize various work principles to perform a single task:
Lock a token on the first blockchain (sender) and create a proof of lock using a bridge contract
Transfer the proof of lock to the second blockchain (receiver), which is verified by this blockchain
A token that corresponds to the token locked on the first blockchain is minted: either a wrapped token or a stablecoin
Wrapped tokens are those that exist on another blockchain, while being secured on the original chain. For example, wrapped Bitcoin (WBTC) is a token with the same price as the original BTC. It is secured by the locked BTC and can be exchanged for it at any moment.
Did you know that GetBlock offers node clusters for compatibility between various chains? Check them out!
Bridges differ in how they lock tokens, create a proof of lock, and route it to the receiver blockchain. Some of them use liquidity pools to ensure token supply, similar to DEXs, while others deploy an off-chain network for transactions or a separate L1 chain with validators.
Examples of crypto bridges
At GetBlock, we have guides for bridging into several blockchain ecosystems, so if you’re interested in specific chains, please check:
There are bridges specialized in transactions between several specific chains, such as Ethereum to Polygon or Ethereum to Sui. Here, we overview only those that support a wide number of chains.
How do we rank the best crypto bridges
As every blockchain bridge has a similar purpose, they can be evaluated using specific metrics.
Core metrics we use
Here are five metrics we’ve used for evaluating each bridge’s performance. They are based on the questions below:
Speed: What is the average transaction speed?
Security: How does the protocol secure funds, and were its contracts audited?
User experience: How easy is it to select the most cost-efficient bridging route?
Liquidity and capacity: How does the bridge ensure liquidity for transactions?
Ecosystem integration: How can the bridge be integrated with other services?
Some protocols offer lower prices, while others report higher speeds. Let's look closer.
Editor pick: Use case summary
Below is a table with a quick summary of each bridge protocol we’ve reviewed as of November 2025.
Bridge | Work principle | Supported chains | Speed | Fees |
Wormhole | Off-chain guardian network | 20+ | Near-instant | Medium |
Stargate | Liquidity pools + contracts | 50+ | Near-instant | Very low |
Synapse | Liquidity pools + contracts | 20+ (EVM) | 1–2 minutes | Low–medium |
Orbiter | Validator layer + aggregation | 40+ | 10-40 seconds | Low |
Axelar | Separate L1 with validators | 80+ | Fast, varies | Medium |
Router | Separate L1 with validators | 10+ | 5–20 seconds | Low |
Rubic | Bridge aggregation layer | 58 | Varies heavily | Usually low |
Bridge vs cross-chain swap
Bridges and swaps are often confused, as they have similar DEX-like mechanics, where one can send one token and receive another, usually with a pre-defined fee. However, they work very differently.
Cross-chain swaps are simply decentralized exchange tools that allow users to sell a token they want to bridge and buy another one using market prices. Unlike them, bridges don’t exchange anything: they route the token directly between chains via the mechanism described above.
Usually, bridges are more efficient compared to cross-chain swaps, as they transfer tokens directly between chains and are much less dependent on market fluctuations. A bridge user should only pay protocol gas fees.
Quick bridge snapshot
Now, we can focus on specific projects and explore the principles of their work.
Wormhole
Rather than being a single bridge, Wormhole is a toolset for cross-chain transfers and communications that can be integrated into other applications. It uses its own off-chain guardian network for transaction processing, which enables lightning-fast speeds.
Source: PortalBridge, powered by Wormhole
Stargate
Stargate Finance is a bridge ecosystem that uses a unified liquidity pool with STG tokens to power all transactions between available blockchains. Due to that, it has very low prices and good usability.
Source: Stargate
Synapse
Synapse Protocol is a DeFi ecosystem that allows swapping and bridging various tokens between EVM networks and uses liquidity pools to secure funds. Users can contribute to them to earn a stable yield.
Source: Synapse
Orbiter
Orbiter Finance aggregates various routing pathways and uses its network of Makers, volunteers who provide computational capacities to enhance cross-chain transactions. Users can apply to become Makers and earn rewards while ensuring quick and fast bridging.
Source: Orbiter Finance
Axelar
Axelar is a separate L1 chain for various purposes related to tokenization and cross-chain interoperability. Similar to Wormhole, it can be easily integrated into applications and used as an efficient cross-chain bridge, supporting a wide range of blockchains.
Source: SquidRouter, powered by Axelar
Router
https://app.routerprotocol.com/
Similarly, Router Protocol is a separate, EVM-compatible L1 chain designed specifically for blockchain interoperability. It has a variety of tools for cross-chain interoperability and can be used in cross-chain dApp development.
Source: Router Protocol
Rubic
Being a bridge aggregator rather than a bridge itself, Rubic is in our list due to its robust user interface that ensures competitive fees and a very broad range of available chains. It aggregates various routing protocols and selects the fastest and cheapest route automatically.
Source: Rubic
How to choose a bridge
As a quick wrap-up, here is a summary of what is important when choosing a bridge.
Define your route
First two questions are:
Which blockchains will you use?
Which tokens do you need to bridge?
After that, think about the context. Do you need to transfer tokens for trading? Or integrate the bridge into your own dApp for some purpose? Or just casually transfer your USDT to a different network because your colleagues use it?
Have your own dApp idea? Don’t waste time, sign up now, and start building—we’ll support you.
For example, Wormhole and Axelar can perfectly be integrated into another dApp, Router Protocol has a wide ecosystem of cross-chain tools, while Orbiter, Stargate, and Rubic offer simple options with competitive prices, each with unique features.
Check fees, limits, time
These three parameters are essential for choosing a bridge, but sometimes you need one of them more than another. For example, for casual transactions, low fees are important, but for institutional traders with large transactions, time is more important, as they need to act quickly.
This is a general guideline, but it will help you understand what bridges can be used for and which case is closest to you.
Conclusion: Making Web3 interconnected
With the rise and development of various blockchains, it’s essential to ensure that all these ecosystems are interconnected and users can move their assets freely as they want. Blockchain bridges, just like physical ones, connect these isolated islands of separate chains, so users can transfer their assets freely. Now, we understand how to select the best bridge for every task and how different projects realize their functions.
As new chains develop, we need robust infrastructure to support their growth—and that’s why GetBlock exists. We support more than 100 chains now and continue to add new ones, ensuring that Web3 devs won’t be stuck. And not only that! We help Web3 projects to promote themselves and enter the market, as ecosystem development is our primary goal. Contact us to share your project and your ideas, and let’s build together.
Popular Posts
June 9, 2021
4 min read
November 9, 2021
5 min read
May 24, 2022
5 min read
March 18, 2021
4 min read